| Article by Oleksandr Korobov, CTO |
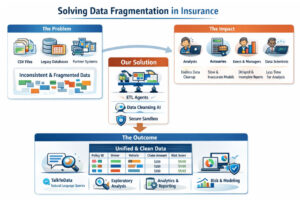
In insurance, data almost never exists as a single, clean dataset that is ready for analysis. In reality, it is spread across CSV files, databases, partner exports, and internal systems. Each source comes with its own structure, naming conventions, data quality, and implicit logic.
This is what we call data fragmentation. It is not always visible, but it steadily slows down analytics, increases operational risk, and raises the real cost of decision-making across the insurance business.
How data fragmentation appears in everyday work
In automotive insurance, fragmentation usually looks like this:
- Multiple CSV files describing policies, claims, vehicles, drivers, pricing, or endorsements.
- Separate databases owned by underwriting, claims, actuarial, finance, and analytics teams.
- Different identifiers and naming conventions for the same business entities.
- Different levels of aggregation, such as policy-level, claim-level, driver-level, or time-based snapshots.
- Business logic hidden inside column names or undocumented transformations.
Each dataset may seem usable on its own. Problems start when these datasets need to be combined into one consistent view.
Who feels the impact
- Business analysts spend a large share of their time reconciling data instead of answering business questions.
- Actuaries face delays and uncertainty when preparing pricing, reserving, or risk models, where small inconsistencies can lead to meaningful financial impact.
- Data analysts and data scientists lose time on manual joins, cleansing, and normalization instead of analysis, modeling, and insight generation.
- Insurance executives and department heads receive insights later than expected, sometimes with caveats that reduce confidence and limit decisive action.
Fragmentation becomes a quiet operational cost paid by everyone who works with data
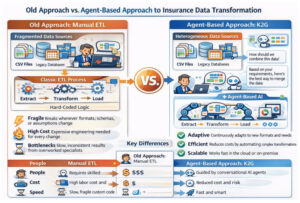
Why traditional ETL is not enough
Classic ETL pipelines can address parts of the problem, but they struggle in real insurance environments.
- They tend to break when input formats change. In fact, depending on users’ request ETL procedure can be different, the same situation we see with dynamically changed source structure.
- They encode assumptions in code instead of making them explicit.
- They require constant involvement of highly specialized engineers.
- They lack understanding of insurance-specific business meaning.
- They move data, but they do not reason about it.
How we approach data fragmentation at K2G
We treat data fragmentation as a reasoning problem, not only a technical one.
Our platform combines ETL agents that ingest data from heterogeneous sources and, through interaction with the user, understand how datasets should be joined, aligned, and aggregated.
On top of that, Data Cleansing agents normalize and standardize the merged data according to insurance domain logic, including policies, vehicles, claims, and risk factors.
All computations run in a secure sandbox. The intelligence behind this process is built on agent-based AI using large language models that can understand structure, intent, and business semantics, not just file formats.
This allows fragmentation to be resolved manually when full control and transparency are required, or automatically when speed and scalability matter. The same approach works both in the cloud and on-premise, depending on regulatory and data sovereignty requirements.
What we get as a result
Solving data fragmentation does not just produce cleaner data.
The outcome is a single, well-structured unified dataset, in our case usually just one table. This dataset becomes a reliable foundation for everything that follows.
- It integrates naturally with the rest of the K2G agent ecosystem.
- It works with TalkToData for natural language queries over consolidated insurance data.
- It feeds Exploratory Data Analysis agents for fast and systematic understanding of distributions, anomalies, and relationships.
- It supports reporting and analytics agents that generate consistent and reproducible reports and dashboards.
- It enables modeling and risk analysis workflows built on a trusted and normalized data layer.
Once fragmentation is addressed, every downstream agent works faster, more accurately, and with fewer assumptions.
Why this matters
Insurance data will always come from many sources. Fragmentation itself is not going away.
The real difference lies in whether an organization can reliably transform fragmented inputs into a single, trustworthy analytical foundation.
By combining insurance domain knowledge, agent-based AI, and secure execution, we turn data fragmentation from a permanent bottleneck into a manageable and repeatable process. This is the problem we focus on, and this is where meaningful leverage in insurance analytics begins.